The terms Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are often used interchangeably, but they are distinct concepts with their own unique characteristics. While both fields contribute to advancements in technology and have a transformative impact on various industries, understanding the key differences between them is crucial for leveraging their potential.
In this article, we will explore Machine Learning vs. Artificial Intelligence, helping you better understand what each term means, how they relate to one another, and how they are applied in real-world scenarios.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the broader concept of machines or systems that can simulate human intelligence. The goal of AI is to enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as problem-solving, decision-making, understanding natural language, and recognizing patterns.
AI can be classified into two categories:
- Narrow AI: Designed to perform a specific task (e.g., voice assistants like Siri).
- General AI: Theoretical at this stage, this would have the ability to perform any cognitive task that a human can do.
AI technologies are used in various sectors, including healthcare, finance, autonomous vehicles, and robotics, to improve efficiency, decision-making, and customer experiences.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
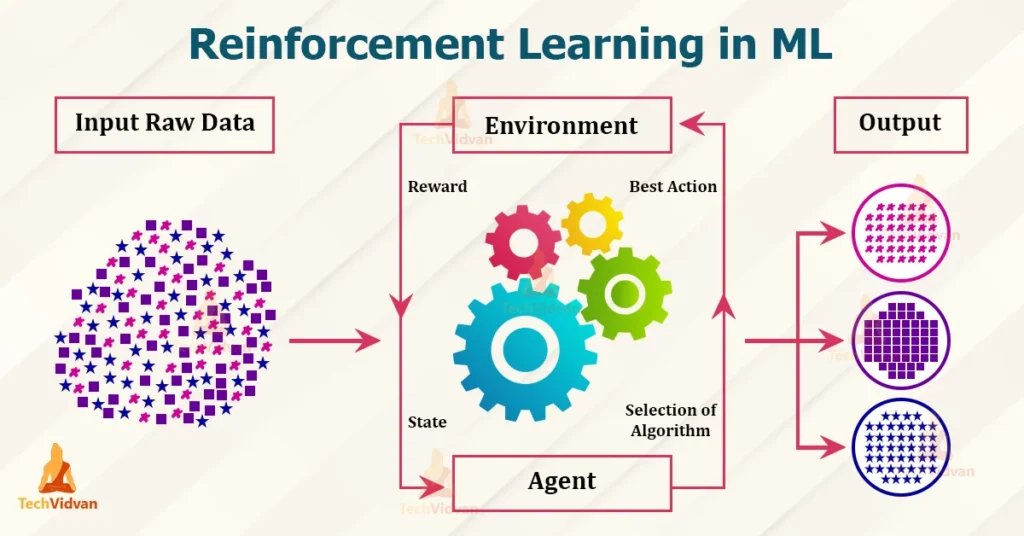
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI). It focuses on the idea that systems can learn from data, improve their performance over time, and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed.
In machine learning, algorithms are trained using large datasets to recognize patterns, make predictions, and solve problems. The more data the system is exposed to, the better it becomes at performing its tasks. Machine learning is used in applications such as recommendation systems (e.g., Netflix, Amazon), fraud detection, spam filtering, and image recognition.
Key Differences Between Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
1. Scope
- Artificial Intelligence is the broader concept that encompasses the development of machines or systems with the ability to perform tasks that require human intelligence.
- Machine Learning, on the other hand, is a subset of AI that focuses specifically on the idea of machines learning from data to make decisions or predictions without being explicitly programmed.
2. Functionality
- AI involves creating systems that can simulate human-like thinking and decision-making. It includes areas like natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and robotics.
- Machine learning, however, focuses on training algorithms using data so that machines can learn from patterns and make data-driven predictions.
3. Goal
- The goal of AI is to create machines that can mimic human intelligence in a variety of tasks, from playing chess to diagnosing diseases.
- The goal of ML is more focused on enabling machines to learn and improve over time through experience and data, which allows them to become more accurate in specific tasks.
4. Approach
- AI encompasses a wide range of approaches, including rule-based systems, expert systems, and genetic algorithms, in addition to machine learning.
- Machine learning relies on statistical models, neural networks, and optimization techniques to process and learn from data.
5. Dependency on Data
- While AI systems can function with or without data, they are more advanced and accurate when data is integrated into their design.
- Machine learning is heavily dependent on data. The success of an ML algorithm is directly related to the quantity and quality of the data it is trained on.
Types of Machine Learning and AI Techniques
Machine Learning Techniques:
- Supervised Learning: The algorithm learns from labeled data to make predictions. It is often used in tasks like image recognition or spam filtering.
- Unsupervised Learning: The algorithm identifies patterns in unlabeled data. It’s useful for tasks like clustering and anomaly detection.
- Reinforcement Learning: This approach uses rewards and punishments to teach machines to make sequences of decisions. It’s commonly used in robotics and game playing.
Artificial Intelligence Techniques:
- Expert Systems: Mimics the decision-making ability of a human expert.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables machines to understand and process human language.
- Computer Vision: AI techniques that allow computers to interpret and analyze visual information from the world.
Real-World Applications of AI and Machine Learning
Applications of Artificial Intelligence:
- Healthcare: AI-powered systems for diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and personalizing treatment plans.
- Autonomous Vehicles: AI helps self-driving cars interpret their environment and make decisions based on real-time data.
- Finance: AI-driven fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and customer service automation.
Applications of Machine Learning:
- Recommendation Systems: Netflix, Amazon, and YouTube use ML algorithms to recommend products, movies, and videos based on user behavior.
- Speech Recognition: ML algorithms improve voice assistants like Siri and Alexa by learning from user interactions.
- Fraud Detection: Machine learning detects fraudulent transactions by analyzing patterns in financial data.
The Relationship Between Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence, but it is one of the key technologies powering many AI-driven applications. While AI seeks to create systems that mimic human intelligence in broad areas, machine learning focuses specifically on the process of learning from data.
In essence, all machine learning is artificial intelligence, but not all AI is machine learning. Machine learning represents one of the most significant advancements in AI, as it allows machines to “learn” and improve from experience.
Also Read: How Ai Is Revolutionizing Healthcare: Innovations And Impacts
Conclusion: Machine Learning vs. Artificial Intelligence
In conclusion, while Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence share common goals of creating intelligent systems, they are distinct concepts. AI is the overarching field that seeks to develop machines that can simulate human intelligence, while machine learning is a specific approach within AI that uses data to help machines learn and improve over time.
Understanding the differences between Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence is essential for businesses, developers, and individuals who want to leverage these technologies in their respective fields. As both AI and ML continue to evolve, their impact on industries such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous systems will continue to grow, creating new opportunities and challenges.
SEO Optimization Tips
- Keyword Placement: Use keywords like “Machine Learning vs Artificial Intelligence,” “AI vs ML,” “difference between AI and ML,” “artificial intelligence,” and “machine learning” naturally within the content, especially in headings and the first 100 words.
- Meta Description: “Explore the key differences between machine learning and artificial intelligence, two transformative technologies that are shaping the future of business and technology.”
- Internal & External Links: Add internal links to related articles on AI, ML, or deep learning, and external links to authoritative sources or studies for credibility.
- Engagement: Encourage readers to comment with their opinions or experiences using AI and ML technologies to boost engagement.